Product Description
JCB SPARE PARTS Backhoe loader 3cx and 4cx FILTER 32/925371
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
A: Generally, we pack our goods in neutral white boxes and brown cartons. If you have legally registered patent,
we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your terms of payment?
A: T/T 30% as deposit, and 70% before delivery. We’ll show you the photos of the products and packages
before you pay the balance.
Q3. What is your terms of delivery?
A: EXW, FOB, CFR, CIF, DDU.
Q4. How about your delivery time?
1) 1-2 days if goods in stock.
2) 10-20 days if goods out of stock with molding.
3) 25-35 days if goods out of stock without molding.
Q5. Can you produce according to the samples?
A: Yes, we can produce by your samples or technical drawings. We can build the molds and fixtures.
Q6. What is your sample policy?
A: We can supply the sample if we have ready parts in stock, but the customers have to pay the sample cost and
the courier cost.
Q7. Do you test all your goods before delivery?
A: Yes, we have 100% test before delivery
Q8: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
A:1. We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit ;
2. We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them,
no matter where they come from.
| 01/117901 | BELT |
| 01/124404 | BELT |
| 01/124405 | BELT |
| 01/130301 | BELT |
| 02/100073 | Filter |
| 02/100078 | GEAR |
| 02/100192 | Thermostat |
| 02/15714 | Filter |
| 02/101327 | BELT |
| 02/101435 | seal |
| 02/101436 | SEAL |
| 02/101440 | ROD |
| 02/101566 | BELT |
| 02/101906 | BELT |
| 02/157140 | WATER PUMP |
| 02/157161 | WATER PUMP |
| 02/192002 | BEARING |
| 02/192003 | BEARING |
| 02/192004 | BEARING |
| 02/192005 | BEARING |
| 02/200002 | CYLINDER |
| 02/20571 | BEARING |
| 02/200018 | PULLEY |
| 02/200113 | Connector |
| 02/200114 | cooler |
| 02/200120 | Cooler oil |
| 02/200173 | SEAL KITS |
| 02/200192 | PISTON RING |
| 02/20571 | Hub Fan Drive |
| 02/20571 | Hub Fan Drive |
| 02/200460 | TURBO |
| 02/200502 | Elbow turbo exhaust |
| 02/200503 | BUSH |
| 02/200521 | BELT |
| 02/2571 | GASKET |
| 02/20 0571 | GASKET |
| 02/20571 | PULLEY |
| 02/200904 | PISTON |
| 02/2571 | CRANKSHAFT |
| 02/257150 | GEAR PUMP |
| 02/201140 | PISTON RING |
| 02/201141 | CYLINDER |
| 02/201142 | Liner slip-fit |
| 02/201291 | BELT |
| 02/201318 | Connector water outlet |
| 02/201328 | PULLEY |
| 02/201343 | CAP |
| 02/201357 | Hub Fan Drive |
| 02/201406 | Connector |
| 02/201452 | Valve oil relief |
| 02/201457 | WATER PUMP |
| 02/201504 | PISTON RING |
| 02/201505 | PISTON |
| 02/201539 | GASKET WATER PUMP |
| 02/201729 | GASKET |
| 02/201804 | PISTON RING |
| 02/201805 | PISTON |
| 02/201823 | TIMING CASE |
| 02/201849 | GASKET |
| 02/201852 | TIMING COVER |
| 02/201858 | Elbow turbo exhaust |
| 02/257107 | Thermostat |
| 02/257117 | Breather |
| 02/257145 | PISTON |
| 02/257174 | TIMING CASE |
| 02/257170 | SEAL |
| 02/257100 | TURBO |
| 02/257111 | Connector water outlet |
| 02/257167 | Connector water outlet |
| 02/257180 | WATER PUMP |
| 02/257184 | HOUSING |
| 02/257185 | GEAR PUMP |
| 02/257110 | WATER PUMP |
| 02/257124 | GASKET |
| 02/257110 | CRANKSHAFT |
| 02/257115 | BEARING |
| 02/257116 | BEARING |
| 02/257117 | BEARING |
| 02/257118 | BEARING |
| 02/257120 | PISTON |
| 02/257121 | PISTON RING |
| 02/257122 | ROD |
| 02/257135 | SEAL |
| 02/257162 | HOUSING |
| 02/257178 | GASKET KITS |
| 02/257180 | Connector water inlet |
| 02/257183 | GASKET |
| 02/257194 | GASKET KITS |
| 02/257199 | GASKET KITS |
| 02/203002 | COOLER GASKET |
| 02/2571 | Elbow exhaust |
| 02/203017 | Gasket exhaust manifold |
| 02/203056 | CYLINDER KITS |
| 02/25716 | COOLER |
| 02/25716 | Top Gasket RG |
| 02/2 0571 0 | TURBO |
| 02/2 0571 6 | CYLINDER KITS |
| 02/2 0571 4 | Connector water outlet assembly vertical |
| 02/2 0571 5 | THERMO |
| 02/2 0571 6 | THERMOSTAT |
| 02/203218 | COOLER GASKET |
| 02/203237 | Cover Ciover timing |
| 02/203246 | TIMNING CASE |
| 02/634780 | LIFT PUMP |
| 02/800571 | filter |
| 02/805712 | BELT |
| 02/857110 | water pump |
| 02/91 0571 | filter |
| 02/971635 | filter |
| 04/55710 | TORQUE CONVERNT |
| 04/55716 | Friction |
| 04/55717 | Friction |
| 04/505717 | GEAR PUMP |
| 04/505719 | FRICTION |
| 04/55711 | Friction |
| 04/55713 | FRICTION |
| 04/55715 | FRICTION |
| 04/500300 | Friction |
| 04/500800 | TORQUE |
| 04/501400 | TORQUE |
| 04/501700 | Friction |
| 04/501800 | TORQUE CONVERNT |
| 04/600650 | TORQUE CONVERNT |
| 04/600784 | TORQUE |
| 04/600786 | TORQUE CONVERNT |
| 04/6 4 | DISC |
| 05/206000 | Bearing roller |
| 05/206300 | Shaft |
| 05/900308 | SEAL KITS |
| 05/901926 | Pad thrust |
| 05/903801 | JS220 GEAR |
| 05/903804 | Gear sun |
| 05/903805 | Gear reduction set 1st planet |
| 05/903806 | Gear reduction set 2nd planet |
| 05/903808 | Gear planet |
| 05/903811 | Seal assembly |
| 05/903819 | O Ring |
| 05/903823 | Gear sun |
| 05/903825 | Gear reduction set 1st planet |
| 05/903854 | Coupling |
| 05/903860 | Gear reduction assembly |
| 05/903862 | Ring Toothed |
| 05/903865 | Ring Toothed |
| 05/903866 | Gear Reduction Assembly |
| 05/903867 | Gear Sun |
| 05/903869 | Shaft pinion 14 teeth |
| 05/903872 | Bearing |
| 05/9 0571 3 | Sun Gear(Swing 2nd) |
| 106/40001 | BOLT |
| 109/55715 | SHAFT |
| 111/35711 | ENGINE MOUNTING |
| 116/00525 | CLIP |
| 120/30002 | COTTER PIN |
| 120/30003 | SHAFT |
| 120/38003 | SPACER |
| 120/40301 | PISTON HOUSIN |
| 120/93201 | HANDLE |
| 120/93202 | HANDLE |
| 1207/0017 | Bush |
| 1207/0019 | Bush |
| 1208/0015 | Bush |
| 1208/0017 | Bush |
| 1208/0018 | Bush |
| 1208/571 | Bush |
| 1208/0571 | Bush |
| 1208/0571 | Bush |
| 1208/571 | Bush |
| 1208/0031 | Bush |
| 1208/0032 | Bush |
| 1209/0019 | Bush |
| 1209/571 | Bush |
| 1209/0571 | Bush |
| 1209/571 | Bush |
| 1209/0571 | Bush |
| 1209/0026 | BUSH |
| 121/13400 | LOCK |
| 121/13500 | LOCK DOOR |
| 121/34400 | Tractor Parts(Plastic etc.,) |
| 121/59400 | MIRROR |
| 121/59800 | TANK |
How to Replace a Bearing
If you want to select a bearing for a specific application, you should know a few basics. This article will give you an overview of ball, angular contact, and sliding-contact bearings. You can choose a bearing according to the application based on the characteristics of its material and preload. If you are not sure how to choose a bearing, try experimenting with it. The next step is to understand the Z-axis, which is the axes along which the bearing moves.
Z axis
When it comes to replacing your Z axis bearing, there are several things you must know. First, you need to make sure that the bearings are seated correctly. Then, you should check the tension and rotation of each one. To ensure that both bearings are equally tensioned, you should flex the Core to the desired angle. This will keep the Z axis perpendicular to the work surface. To do this, first remove the Z axis bearing from its housing and insert it into the Z axis motor plate. Next, insert the flanged bearing into the Z axis motor plate and secure it with 2 M5x8mm button head cap screws.
Make sure that the bearing plate and the Z Coupler part are flush and have equal spacing. The spacing between the 2 parts is important, as too much spacing will cause the leadscrew to become tight. The screws should be very loose, with the exception of the ones that engage the nylocks. After installing the bearing, the next step is to start the Z axis. Once this is done, you’ll be able to move it around with a stepper.
Angular contact
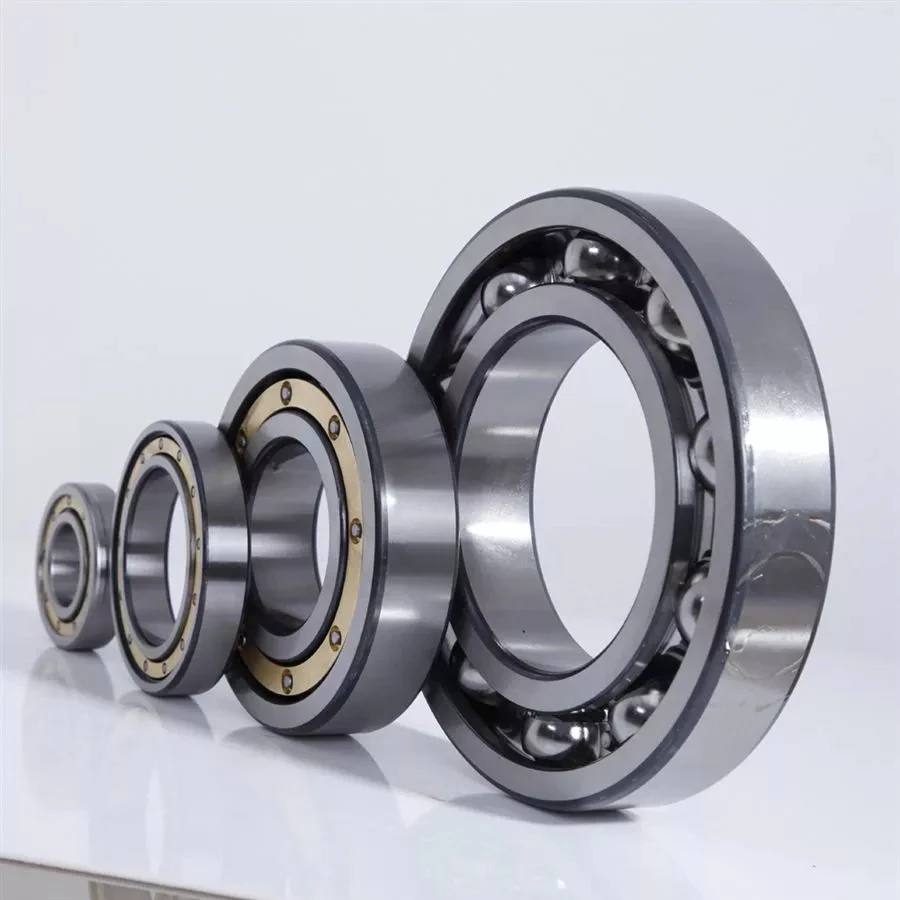

Ball bearings are made with angular contacts that result in an angle between the bearing’s races. While the axial load moves in 1 direction through the bearing, the radial load follows a curved path, tending to separate the races axially. In order to minimize this frictional effect, angular contact bearings are designed with the same contact angle on the inner and outer races. The contact angle must be chosen to match the relative proportions of the axial and radial loads. Generally, a larger contact angle supports a higher axial load, while reducing radial load.
Ball bearings are the most common type of angular contact bearings. Angular contact ball bearings are used in many applications, but their primary purpose is in the spindle of a machine tool. These bearings are suitable for high-speed, precision rotation. Their radial load capacity is proportional to the angular contact angle, so larger contact angles tend to enlarge with speed. Angular contact ball bearings are available in single and double-row configurations.
Angular contact ball bearings are a great choice for applications that involve axial loads and complex shapes. These bearings have raceways on the inner and outer rings and mutual displacement along the axial axis. Their axial load bearing capacity increases as the contact Angle a rises. Angular contact ball bearings can withstand loads up to 5 times their initial weight! For those who are new to bearings, there are many resources online dedicated to the subject.
Despite their complexity, angular contact ball bearings are highly versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications. Their angular contact enables them to withstand moderate radial and thrust loads. Unlike some other bearings, angular contact ball bearings can be positioned in tandem to reduce friction. They also feature a preload mechanism that removes excess play while the bearing is in use.
Angular contact ball bearings are made with different lubricants and cage materials. Standard cages for angular contact ball bearings correspond to Table 1. Some are machined synthetic resins while others are molded polyamide. These cage materials are used to further enhance the bearing’s axial load capacity. Further, angular contact ball bearings can withstand high speeds and radial loads. Compared to radial contact ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings offer the greatest flexibility.
Ball bearings
Ball bearings are circular structures with 2 separate rings. The smaller ring is mounted on a shaft. The inner ring has a groove on the outer diameter that acts as a path for the balls. Both the inner and outer ring surfaces are finished with very high precision and tolerance. The outer ring is the circular structure with the rolling elements. These elements can take many forms. The inner and outer races are generally made of steel or ceramic.
Silicon nitride ceramic balls have good corrosion resistance and lightweight, but are more expensive than aluminum oxide balls. They also exhibit an insulating effect and are self-lubricating. Silicon nitride is also suitable for high-temperature environments. However, this type of material has the disadvantage of wearing out rapidly and is prone to cracking and shattering, as is the case with bearing steel and glass. It’s also less resistant to heat than aluminum oxide, so it’s best to buy aluminum nitride or ceramic ball bearings for applications that are subjected to extremely high temperatures.
Another type of ball bearings is the thrust bearing. It has a special design that accommodates forces in both axial and radial directions. It is also called a bidirectional bearing because its races are side-by-side. Axial ball bearings use a side-by-side design, and axial balls are used when the loads are transmitted through the wheel. However, they have poor axial support and are prone to separating during heavy radial loads.
The basic idea behind ball bearings is to reduce friction. By reducing friction, you’ll be able to transfer more energy, have less erosion, and improve the life of your machine. With today’s advances in technology, ball bearings can perform better than ever before. From iron to steel to plastics, the materials used in bearings have improved dramatically. Bearings may also incorporate an electromagnetic field. So, it’s best to select the right 1 for your machine.
The life expectancy of ball bearings depends on many factors, including the operating speed, lubrication, and temperature. A single million-rpm ball bearing can handle between 1 and 5 million rotations. As long as its surface contact area is as small as possible, it’s likely to be serviceable for at least 1 million rotations. However, the average lifespan of ball bearings depends on the application and operating conditions. Fortunately, most bearings can handle a million or more rotations before they start showing signs of fatigue.
Sliding-contact bearings

The basic principle behind sliding-contact bearings is that 2 surfaces move in contact with 1 another. This type of bearing works best in situations where the surfaces are made of dissimilar materials. For instance, a steel shaft shouldn’t run in a bronze-lined bore, or vice versa. Instead, 1 element should be harder than the other, since wear would concentrate in that area. In addition, abrasive particles tend to force themselves into the softer surface, causing a groove to wear in that part.
Sliding-contact bearings have low coefficients of friction and are commonly used in low-speed applications. Unlike ball and roller bearings, sliding contact bearings have to be lubricated on both sides of the contacting surfaces to minimize wear and tear. Sliding-contact bearings generally are made of ceramics, brass, and polymers. Because of their lower friction, they are less accurate than rolling-element bearings.
Sliding-contact bearings are also known as plain or sleeve bearings. They have a sliding motion between their 2 surfaces, which is reduced by lubrication. This type of bearing is often used in rotary applications and as guide mechanisms. In addition to providing sliding action, sliding-contact bearings are self-lubricating and have high load-carrying capacities. They are typically available in 2 different types: plain bearings and thrust bearings.
Sliding-contact linear bearing systems consist of a moving structure (called the carriage or slide) and the surfaces on which the 2 elements slide. The surfaces on which the bearing and journal move are called rails, ways, or guides. A bore hole is a complex geometry, and a minimum oil film thickness h0 is usually used at the line of centers. It is possible to have a sliding-contact bearing in a pillow block.
Because these bearings are porous, they can absorb 15 to 30% of the lubrication oil. This material is commonly used in automobile and machine tools. Many non-metallic materials are used as bearings. One example is rubber, which offers excellent shock absorbency and embeddability. While rubber has poor strength and thermal conductivity, it is commonly used in deep-well pumps and centrifugal pumps. This material has high impact strength, but is not as rigid as steel.

